Combined 3D Reconstruction and Semantic Segmentation Using Deep Learning and Multi-angle Aerial Imagery
A 3D city model is a digital model of an urban space which contains accurate 3D information of individual buildings and associated structures. 3D city models are used to assist in urban planning, monitoring building extensions and renovations. A good 3D city model accurately models the external structure and footprint of the building and provides a high-fidelity visualization of the building from various perspectives.
However, imperfections such as incomplete surface, twisted mirror-like surface and imprecise building edges and corners can occur in certain scenarios.
The goal of the project is to construct a 3D photo-textured mesh from multi-angle aerial photography which exploits semantics to produce more precise building structure, which is useful for downstream tasks and ultimately, develop a pipeline for 3D reconstruction of complex urban objects that is more accurate than traditional photogrammetry techniques.
3D reconstruction of urban environments in important for in applications including robotics and other autonomous vehicles that use sensor data to perceive their environment.
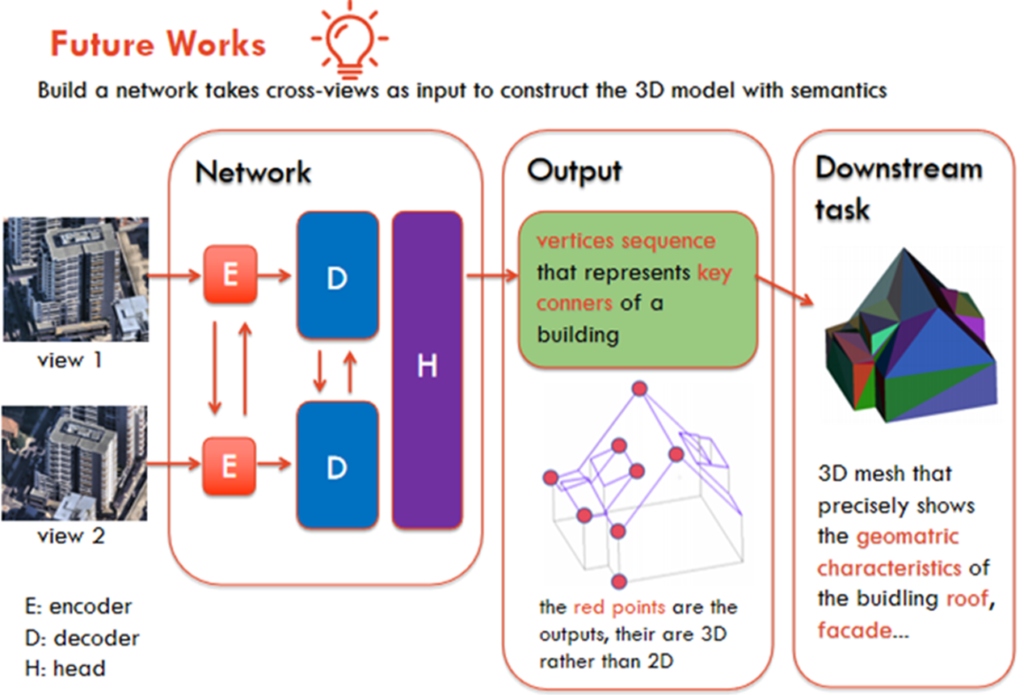
Research Activities:
Research is focusing on using supervised machine learning approaches to (a) predict 3D structure from multi-perspective imagery and (b) predict geometric mesh information and CAD-style models from visual and 3D information derived from images.
Expected Impact:
The research will build on the recent powerful deep learning-based 3D reconstruction algorithms, which allow us to leverage semantic information to further improve precision in 3D reconstruction. The research is expected to make new contributions to approaches to learn precise 3D information from images. The research is also expected to streamline the process of determining building and other urban structural measurements from images that are free imperfections and artefacts present when using traditional photogrammetry approaches that ignore the semantic content in images during reconstruction. Outcomes of the research are also expected to be of benefit to 3D reconstruction pipelines for applications including robotics, mapping system, industrial assembly line etc.
Associated Researchers
-
Mitch Bryson
Chief Investigator
View Bio

